HOMO NALEDI

WITH THE DISCOVERY OF NEW SPECIES HOMO NALEDI IN SOUTH AFRICAN CAVES ANTHROPOLOGISTS ARE ANALZING HUMAN ORIGINS.

IF YOU WANT A GOOD LOOK AT YOUR ELDER COUSINS HERE THEY ARE:
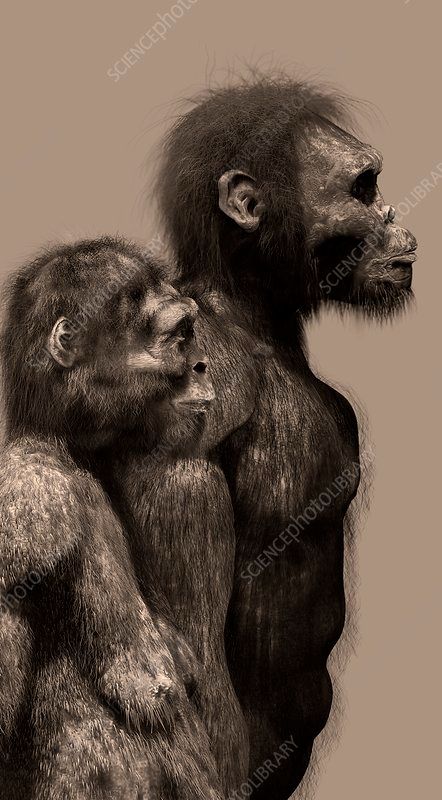

An international team of scientists has discovered a new species of human relative, Homo naledi, which appears to demonstrate that modern humans are not unique in practicing ritualized treatment of the dead.

“Homo naledi is an extraordinary new discovery, both in terms of the unique combination of features found in its skeleton and its inferred behavior,” said William Harcourt-Smith, a co-author on the paper who is a resident research associate in the Museum’s Division of Paleontology and an assistant professor at CUNY’s Lehman College.
The initial discovery was made in 2013 in a cave known as Rising Star in the Cradle of Humankind World Heritage Site, some 50 kilometers (30 miles) northwest of Johannesburg, South Africa, by University of the Witwatersrand scientists and six cavers who are being called “underground astronauts.”
H. naledi was named after the location: “naledi” means “star” in the local Sesotho language. The finds were announced earlier today by the University of the Witwatersrand, the National Geographic Society, and the South African National Research Foundation and described in two papers published in the journal eLife.
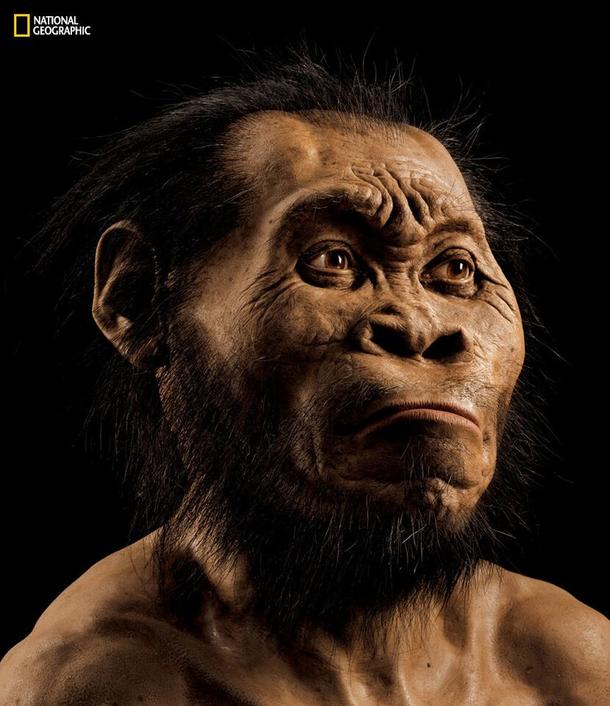

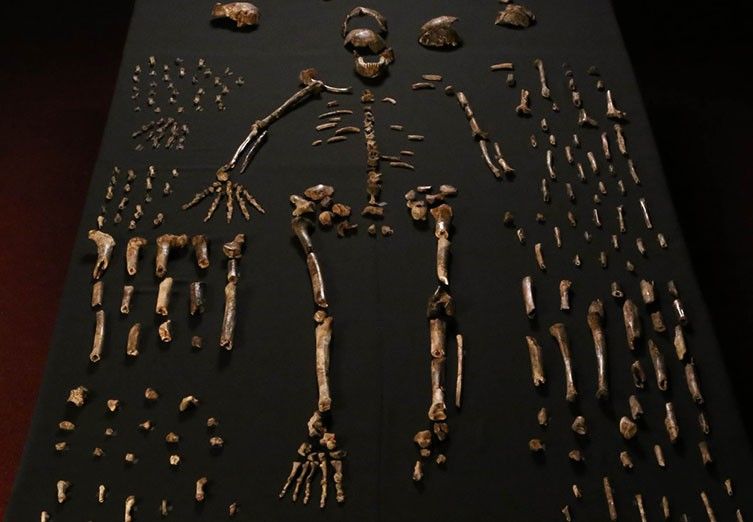
The discovery of hundreds of Homo naledi fossils was the largest such find ever made on the African continent. The fossils display a unique mix of modern and archaic traits and are shaking up our understanding of the origins and diversity of our human lineage.
Homo naledi highlights, once again, that we can't think of human evolution in terms of ape-like ancestors gradually evolving more modern features in a linear fashion. Instead, multiple human species evolved in parallel and coexisted, sometimes side-by-side.
Many mysteries surround Homo naledi, including how the remains got into the caves, what its tools were like, and how it survived alongside bigger-brained species.
Homo naledi discovery: excavations deep within a cave
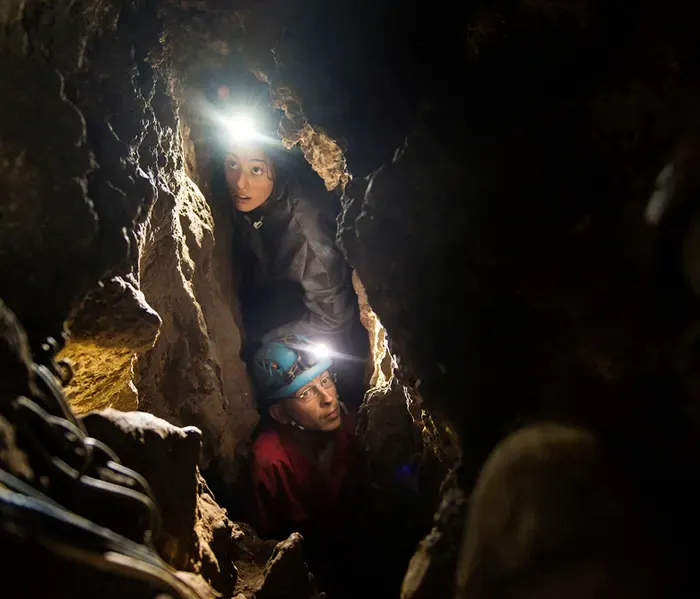
The first Homo naledi finds were discovered by cavers in a remote, almost inaccessible chamber deep within the Rising Star cave system.
Palaeoanthropologist Lee Berger assembled a team of excavators who proceeded to recover more than 1,500 fossil bones belonging to at least 15 individuals, ranging from infants to elderly adults.
This video by Wits University (featuring recreational caver Rick Hunter who discovered the chamber) highlights just how difficult to reach the fossils were, and why the initial team sent to search for fossils was made up of smaller women:

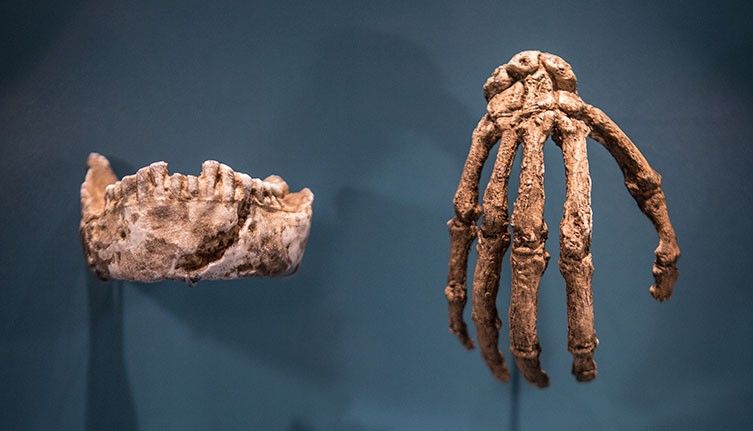
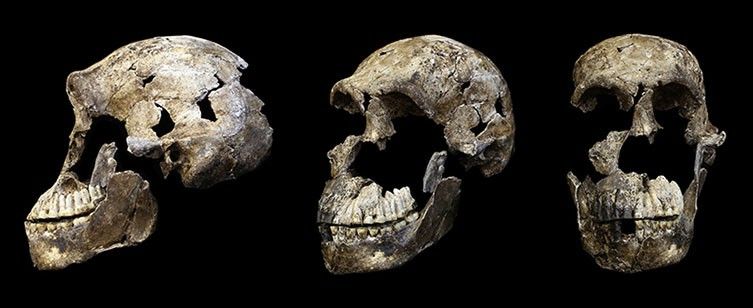
Two Homo naledi mandibles (lower jawbones). The teeth are small and this species' jawbone is not as strongly built as those of many ancient humans and other extinct hominins, but the way the molars increase in size towards the back of the jaw is a notably primitive feature. © Hawks et al (2017) eLife.
'The mixture of traits of Homo naledi highlights once again the complexity of the human family tree,' says Prof Stringer.
Together, H. naledi's anatomy suggests it walked on two legs with a modern gait and an efficient long-distance stride. Its shoulder position and shape of its fingers would have helped it climb and hang from trees and could be traits retained from a more ape-like ancestor.

Where did Homo naledi live?
Because H. naledi is currently only known from two sites within a single cave system, it is unclear whether the species lived only in southern Africa or was more widespread.
If it was more widespread, scientists might need to re-examine other diminutive fossils from across Africa that have often (and perhaps wrongly) been attributed to a small form of Homo erectus, another early human species.
The surprisingly young age of Homo naledi
It took a while for the Homo naledi remains to be dated. The age published in 2017 took scientists by surprise: they were between 236,000 and 335,000 years old.
'This is astonishingly young for a species that still displays primitive characteristics found in fossils about two million years old,' says Prof Stringer.
Despite the young date for the H. naledi fossils, their anatomy suggests that in evolutionary terms they could lie close to the origin of the genus Homo, suggesting that this is a relic species, retaining many primitive traits.
Importantly, the young age means Homo naledi was living on the African continent with a number of other bigger-brained humans, including our own species Homo sapiens.
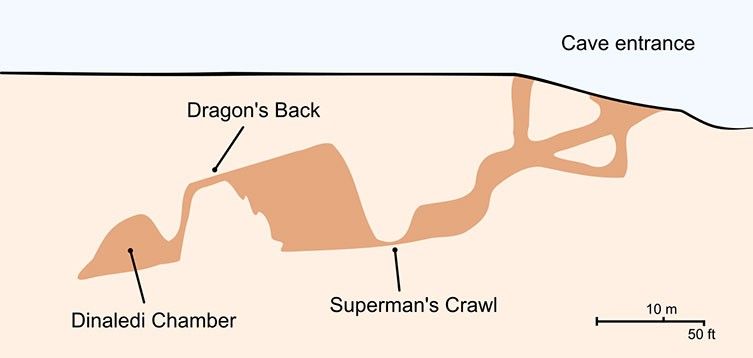
How did the bones get into the cave?
How Homo naledi remains got to their final resting place is a matter of active debate.
The Dinaledi Chamber where they were found is located deep within the cave system - around 80 metres from any known entrance or opening to the surface - and must have always been in in darkness.
The discovery of at least three more individuals in the Lesedi Chamber, equally remote and dark and over 100 metres away, further adds to the mystery.
How did Homo naledi survive against bigger-brained competition?
The teeth and lower body skeleton suggest Homo naledi may have had a lifestyle and diet similar to other hunter-gatherers present elsewhere in Africa at the same time, such as late Homo heidelbergensis and early Homo sapiens.
Although we do have another example of a small-brained species surviving until relatively recently - the diminutive Homo floresiensis in Indonesia - that probably survived because it was isolated on an island.
'Perhaps Homo naledi was relatively geographically isolated for much of its evolutionary history,' says Prof Stringer.
'Or did it avoid competition by continuing a different niche for feeding and lifestyle, allowing it to survive longer? It could have spent more time feeding in and around trees, as might be indicated by its upper body skeleton and curved fingers.'
THINGS YOU MAY NOT KNOW: The timeline of human existence. Their is so much written about the evoution of man plus outerspace involvement and biblical interpations...even modern day anthropologists and scientists debate the exact timeline of our family tree.
THINGS YOU MAY WANT TO SAVE: bones, skeltons, and burial sites.
ZENTRAVELER SAYS: We are lucky to have big brains too bad the politicans missed out?
From here to Infinity is a relatively short ride! The next leg takes eons and eons as you fly through the Barycentric Dynamical Time Zone! …and on and on and on. Follow the Zentraveler Newsletter often for Travel, Health and Zen-like stories and such. Where else can you get a THREE IN ONE NEWSLETTER FOR THE PRICE OF FREE.

ZENTRAVELER IS A PERSONAL NEWSLETTER, DESIGNED TO GIVE TRAVEL, HEALTH, WRITING AND HUMOR INCLUDING HELPFUL HINTS WITH A ZEN LIKE QUALITY.
